Construction And Working Of DC motor
Construction And Working Of DC motor
A motor is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
CONSTRUCTION:
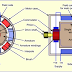
A DC machine consists two basic parts - stator and rotor. Basic constructional parts of a DC machine are described below.
Yoke:
The outer frame of a dc machine is called as yoke. It is made up of cast iron or steel. It not only provides mechanical strength to the whole assembly but also carries the magnetic flux produced by the field winding.
Poles and pole shoes:
Poles are joined to the yoke with the help of bolts or welding. They carry field winding and pole shoes are fastened to them. Pole shoes serve two purposes; (i) they support field coils and (ii) spread out the flux in air gap uniformly.
Field winding:
They are usually made of copper. Field coils are former wound and placed on each pole and are connected in series. They are wound in such way that, when energized, they form alternate North and South poles.
Armature core: Rotor
Armature core is the rotor of the machine. It is cylindrical in shape with slots to carry armature winding. The armature is built up of thin laminated circular steel disks for reducing eddy current losses. It may be provided with air ducts for the axial air flow for cooling purposes. Armature is keyed to the shaft.
Armature winding:
It is usually a former wound copper coil which rests in armature slots. The armature conductors are insulated from each other and also from the armature core. Armature winding can be wound by one of the two methods; lap winding or wave winding. Double layer lap or wave windings are generally used. A double layer winding means that each armature slot will carry two different coils.
Commutator and brushes:
Physical connection to the armature winding is made through a commutator-brush arrangement. The function of a commutator, in a dc generator, is to collect the current generated in armature conductors. Whereas, in case of a dc motor, commutator helps in providing current to the armature conductors. A commutator consists of a set of copper segments which are insulated from each other. The number of segments is equal to the number of armature coils. Each segment is connected to an armature coil and the commutator is keyed to the shaft. Brushes are usually made from carbon or graphite. They rest on commutator segments and slide on the segments when the commutator rotates keeping the physical contact to collect or supply the current.
DC Motor Vs DC Generator
Construction of DC Motor and DC Generator is same
And both are called as DC machine.
Working Principle of DC Motor :
Working Principle Of A DC Motor
A motor is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The principle of working of a DC motor is that "whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force". The direction of this force is given by Fleming's left hand rule and it's magnitude is given by F = BIL. Where, B = magnetic flux density, I = current and L = length of the conductor within the magnetic field.
Fleming's left hand rule: If we stretch the first finger, second finger and thumb of our left hand to be perpendicular to each other AND direction of magnetic field is represented by the first finger, direction of the current is represented by second finger then the thumb represents the direction of the force experienced by the current carrying conductor.
Working of DC Motor
When armature windings are connected to a DC supply, current sets up in the winding. Magnetic field may be provided by field winding (electromagnetism) or by using permanent magnets. In this case, current carrying armature conductors experience force due to the magnetic field, according to the principle stated above.
Commutator is made segmented to achieve unidirectional torque. Otherwise, the direction of force would have reversed every time when the direction of movement of conductor is reversed the magnetic field.













No comments :
Post a Comment