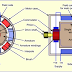
Working principle of three phase induction motor base on the electromagnetic induction.In which stator rotating field cuts the rotor conductor, due to this EMF induced in rotor which produce opposite current in rotor .This effect causes rotation of three phase induction motor.
Explain working principle of three phase induction motor
When three phase supply is connected to the three phase stator winding A rotating magnetic field (flux) is produced.
The magnetic fields rotates at the synchronous speed (Ns) given by
Ns=120*f/p r.p.m
Where f = supply frequency
P = number of pole
This rotating flux passes through the air gap and also flows over the motor surface.
As the Rotor is stationary,This rotating flux cuts the stationary rotor conductors.
Due to the relative velocity between rotor conductor and rotating magnetic field, An EMF will be induced in the rotor conductors.
The magnitude of this in the induced EMF will be Proportional to the Relative speed between rotor and magnetic field.
As the rotor conductors forms the closed circuit,A current start flowing in the rotor circuit.
By lens law the direction of this current is such that is tries to oppose the reason producing it.
As a rotation of magnetic field is the cause, the rotor conductor will experience A force which start rotating the rotor in the same direction As that of flux and tries to reach the speed of magnetic field To reduce the relative velocity and has a induced EMF is zero.
In induction motor stator field rotates at the synchronous speed And thus produces rotor current (or Rotor torque).It is because of relative difference in speed of rotor and stator field.
The rotor current or torque rotates the rotor in the direction of the stator field (RMF),So that the cause which is producing the current or torque can be opposed.
But if the rotor reaches the synchronous speed then the relative speed between rotor and stator field will become zero.
And hence no rotor current or torque Will be produced to maintain the rotation of Rotor.Hance a rotor always lags behind the status field.That mean rotor speed is always less than synchronous speed.