Electrical Fundamentals
Electrical Fundamentals
In electrical fundamentals topic you learn about
- what is electricity
- electric charge
- electric current
- type of current
- electric voltage
1-What is electricity: Electricity is a type of energy which have power. But electrical energy directly not used in any application, electrical energy is generally converted into another form of energy or force.for example:
when we supply electrical energy to a motor, there in electrical energy converted to electromagnetic energy which produced magnetic field in motor. Now electromagnetic flux/field produce torque in motor then motor run.
more examples: electrical convert to light (device light display etc)
electrical to sound, electrical to torque, electrical to electromagnetic field etc.
2-Electric charge: Electric charge is a property of an electron. there are two type of charge exist in an atom one is protones consist positive charge and another is electron consist Negative charge. And Neutron are neutral in nuclear present in center of an atom.You know electric current flows in only good conductor this is due to electron and proton present in an atom. if electron and proton is same then no electron flow this material called bad conductor.if electron is more than proton then it is good conductor or vice-versa.
unit: coulomb
3-Electric current: Electric current is flow of electron in a conductor.When electron of an atom is flow in any one direction then it is called as electric current flow in conductor.Electric current flow in material which have free electron. And free electron are available in only good conductors .overall to know, electron flow in conductor is current.
unit: Ampare
4-Current are two type: AC And DC
AC current: The current which change direction sinusoidal with time is Alternating current.DC current: The current which not change direction with time is Direct current.
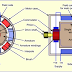
5-Electric voltage: Electric voltage is potential difference between two source.It is also called emf,voltage,potential difference. unit is volt.Voltage produces flow of current. Current flow in direction from high potential source to low potential source. ex. current flow from positIve to negative direction in case of DC . In case of AC current flow from phase wire to ground or earth.
As shown in above figure electron flow from negative charge to positive charge.but direction of current consider as always opposite to it.Mean current flow from positive to negative direction.













No comments :
Post a Comment