Types of DC Generator | series dc generator | shunt dc generator | compound dc generator
DC Generator are classified on the basis of their winding assembling. Means how to stator and armature winding connected it may be series or parallel or both. here you learn and understand Types of DC Generator | series dc generator | shunt dc generator | compound dc generator.
Types of DC Generator with diagram
Generators are classified as follows:
1) Parmanent Magnet DC Generator
2) Sepratly Excited DC Generator
3) Self Excited DC Generator
Self Excited DC Generator are 3 types:
1. Shunt wound generator
2. Series wound generator
3. Compound DC Generator
Compound DC Generator are 2 types:
(1) Short shunt
(2) Long shunt
Detail of the Types of DC Generator | series dc generator | shunt dc generator | compound dc generator:
1) Permanent Magnet DC Generator:
Parmanent magnet is used for flux.
(you can read detail we already posted)
2) Sepretly Excited DC Generator:
DC Generator in which field winding is supplied from an external DC source (EX. battery) is called a separately excited DC generator.
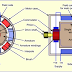
Figure shows the connections of a separately excited generator. The voltage output depends upon the speed of rotation of armature and the field current (Eg = φZNP/60 A). Larger the field current and speed, larger is the generated e.m.f.
Separately excited DC generators are rarely used in practice.Normally of self excited type used.
Armature current, Ia = IL
Terminal voltage, V = Eg - IaRa
Electric power developed = EgIa
Power delivered to load = EgIa - I R = I E - I R = VIa
3) Self Excited DC Generator
3.1) Shunt-Wound DC generator
When the field winding of a generator is connected in parallel with the generator armature, the generator is called a shunt-wound generator .
The excitation current in ashunt-wound generator is dependent upon the output voltage and the field resistance. Normally, field excitation is maintained between 0.5 and 5 percent of the total current output of the generator.
Shunt field current, Ish = V/Rsh
Armature current, Ia = IL + Ish
Terminal voltage, V = Eg - IaRa
Power developed in armature = EgIa
Power delivered to load = VIL
3.2) Series Wound DC Generator
When the field winding of a DC generator is connected in series with the armature, the generator is called a series-wound generator . The excitation current in a series-wound generator is the same as the current the generator delivers to the load. If the load has a high resistance and only draws a small amount of current, the excitation current is also small. Therefore, the magnetic field of the series field winding is weak, making the generated voltage low.
Conversely, if the load draws a large current, the excitation current is also high. Therefore, the magnetic field of the series field winding is very strong, and the generated voltage is high.
Armature current, Ia = Ise = IL = I
Terminal voltage, V = EG - I(Ra + Rse)
Power developed in armature = EgIa
3.3) Compound DC Generator:
In a compound-wound generator, there are two sets of field windings on each pole - one is in series and the other in parallel with the armature. A compound wound generator may be:
Short Shunt : In which only shunt field winding is in parallel with the armature winding.
Long Shunt : In which shunt field winding is in parallel with both series field and armature winding.
1. Short Shunt Compound DC Generator:
Short shunt
Series field current, Ise = IL
Shunt field current,
Terminal voltage, V = Eg - IaRa - IseRse
Power developed in armature = EgIa
2. Long Shunt Compound DC Generator:
Long shunt
Series field current, Ise = Ia = IL + Ish
Shunt field current, Ish = V/Rsh
Terminal voltage, V = Eg - Ia(Ra + Rse)
Power developed in armature = EgIa
Power delivered to load = VIL
EXTRA:
In a compound generator the major portion of excitation is usually supplied by the shunt field. The shunt field is slightly weaker and the series field is considerably weaker than those of the corresponding machine in which the entire excitation is produced by a single shunt or a single series winding.
Compound wound generators are of two types:
1) Cumulative wound Generator : In cumulative wound generators the series field assists the shund field
2) Differential wound Generator : In differential wound generators, series field opposes the shunt field.

















No comments :
Post a Comment