Basic Electrical Engineering
Basic Electrical Engineering
Electricity is a type of power which is ,in old day electrical energy is not in control of human being mean they cant transfer or utilized electrical energy ,now day electrical energy is controlled by human . we can generate in different form such as ac or dc. and used for desire level or for different applications.
Electrical energy flow as.
generation>>transmission>>
Basic Electrical Engineering concepts
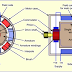
In each plant, the mechanical movement of different equipments is caused by an electric prime mover (motor). Electrical power is derived from either utilities or internal generators and is distributed through transformers to deliver usable voltage levels.
In each plant, the mechanical movement of different equipments is caused by an electric prime mover (motor). Electrical power is derived from either utilities or internal generators and is distributed through transformers to deliver usable voltage levels.
Electricity is found in two common forms:
• AC (alternating current)
• DC (direct current).
Electrical equipments can run on either of the AC/DC forms of electrical energies. The selection of energy source for equipment depends on its application requirements. Each energy source has its own merits and demerits
.
Industrial AC voltage levels are roughly defined as LV (low voltage) and HV (high voltage) with frequency of 50–60 Hz. An electrical circuit has the following three basic components irrespective of its electrical energy form:
- • Voltage (volts)
- • Ampere (amps)
- • Resistance (ohms)
Electrical Quantities:
1.Voltage <unit-volt>
Voltage is defined as the electrical potential difference that causes electrons to flow.
Voltage is defined as the electrical potential difference that causes electrons to flow.
2. Current <unit-ampare>
Vurrent is defined as the flow of electrons and is measured in amperes.
Vurrent is defined as the flow of electrons and is measured in amperes.
3. Resistance <unit-ohm>
Resistance is defined as the opposition to the flow of electrons and is measured in ohms.
Resistance is defined as the opposition to the flow of electrons and is measured in ohms.
Ohm's law = state that voltage (V) is directly proportional to current (I) with contant temperature and pressure.
All three are bound together with Ohm’s law, which gives the following relation between the three:
V = I × R.













No comments :
Post a Comment