Concept of Power
Concept of Power
(a) Power
In DC circuits, power (watts) is simply a product of voltage and current.
P =V × I (unit=watt)
For AC circuits, the formula holds true for purely resistive circuits; however, for the following types of AC circuits, power is not just a product of voltage and current.
In ac circuit different type of current fount due to different application load such as resistive load, inductive load, capacitive load.
In ac circuit different type of current fount due to different application load such as resistive load, inductive load, capacitive load.
1) Apparent power
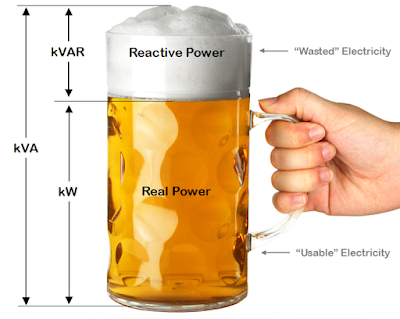
Apparent power is the product of voltage and ampere, i.e., VA or( kVA) is known as apparent power. Apparent power is total power supplied to a circuit inclusive of the true and reactive power.
P=V×I
2) Real power
Real power or true power is the power that can be converted into work and is measured in watts(w)
P=V×I× cosφ
3) Reactive power
Reactive power If the circuit is of an inductive or capacitive type, then the reactive component consumes power and cannot be converted into work. This is known as reactive power and is denoted by the unit (VAR.)
P=V× I× sinφ
(b) Relationship between powers
- Apparent power (VA) = V × A
- True power (Watts) = VA × cosφ
- Reactive power (VAR) = VA × sinφ
(c) Power factor
Power factor is defined as the ratio of real power to apparent power. The maximum value it can carry is either 1 or 100(%), which would be obtained in a purely resistive circuit.
Power factor = True power / Apparent power
p.f=cosφ
Share this post to your friends by this they know types of power
Read BASIC ELECTRICAL Multiple choice question
Read BASIC ELECTRICAL Multiple choice question












No comments :
Post a Comment